lv display | Display (lv lv display lvdisplay shows the attributes of LVs, like size, read/write status, snapshot information, etc. lvs (8) is a preferred alternative that shows the same information and more, using a more compact and configurable output format. Datejust 41. Oyster, 41 mm, Oystersteel and yellow gold. Reference 126333. View in night mode. View variations. Make a date of a day. This Oyster Perpetual Datejust 41 in Oystersteel and yellow gold features a champagne-colour dial and a Jubilee bracelet. Fluted bezel. A Rolex signature. The Rolex fluted bezel is a mark of distinction.
0 · lvdisplay(8) — Linux manual page
1 · Display (lv
2 · 5.4.13. Displaying Logical Volumes
The Diver 300M Chronograph. In addition to three-hand timepieces, the Diver 300M is also available as a chronograph. Omega offers models with two or three subdials, as well as versions with a GMT function. You can purchase the 44-mm watch with three subdials for as little as 4,400 USD on Chrono24.
lvdisplay shows the attributes of LVs, like size, read/write status, snapshot information, etc. lvs (8) is a preferred alternative that shows the same information and more, using a more compact .
 — Linux manual page .jpg)
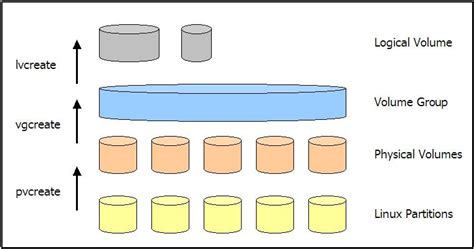
There are three commands you can use to display properties of LVM logical volumes: lvs, lvdisplay, and lvscan. The lvs command provides logical volume information in a configurable .In LVGL, an lv_display_t (not to be confused with a Screen) is a data type that represents a single display panel — the hardware that displays LVGL-rendered pixels on your device. During .
In this tutorial we explore lvdisplay command which is used to display the logical volume status and many other details such as name, UUID, status, size etc.
lvdisplay shows the attributes of LVs, like size, read/write status, snapshot information, etc. lvs (8) is a preferred alternative that shows the same information and more, using a more compact and configurable output format.There are three commands you can use to display properties of LVM logical volumes: lvs, lvdisplay, and lvscan. The lvs command provides logical volume information in a configurable form, displaying one line per logical volume.In LVGL, an lv_display_t (not to be confused with a Screen) is a data type that represents a single display panel — the hardware that displays LVGL-rendered pixels on your device. During system initialization, you must do the following for each display panel you want LVGL to use: create an lv_display_t object for it, assign a Flush Callback .
lvdisplay [1] allows to Display information about a logical volume (LV) and it is part of Linux LVM implementation. # lvdisplay With no arguments will display all your LVs. # lvdisplay /dev/vg0/lv-0. --- Logical volume --- LV Path /dev/vg0/lv-0. LV Name lv-0. VG Name vg0. This command is used to display information about Logical Volume Manager (LVM) logical volumes. It is a useful tool for managing storage systems and analyzing the configuration of logical volumes. The lvdisplay command provides details such as the logical volume name, volume group, size, allocation type, and more. Command: lvdisplay. We have seen above how to create LV, now we will see how to view details of it. This command is the same as pvdisplay for PV and vgdisplay for VG. It shows you details like name, volume group it belongs to, size, permission, status, allocation policy, etc. # lvdisplay /dev/vg01/lvol1. --- Logical volumes ---
If you want to see the details of the volume in a Volume Group, you can use the lvdisplay command. Below is an example of lvdisplay command. Here, Vol1 is the Volume Group name. $ sudo lvdisplay Vol1. --- Logical volume --- LV Path /dev/Vol1/lvtest. LV .lvdisplay shows the attributes of LVs, like size, read/write status, snapshot information, etc. lvs (8) is a preferred alternative that shows the same information and more, using a more compact and configurable output format.lvdisplay allows you to see the attributes of a logical volume like size, read/write status, snapshot information etc. lvs (8) is an alternative that provides the same information in the style of ps (1). lvs (8) is recommended over lvdisplay. In this tutorial we explore lvdisplay command which is used to display the logical volume status and many other details such as name, UUID, status, size etc.
lvdisplay shows the attributes of LVs, like size, read/write status, snapshot information, etc. lvs (8) is a preferred alternative that shows the same information and more, using a more compact and configurable output format.There are three commands you can use to display properties of LVM logical volumes: lvs, lvdisplay, and lvscan. The lvs command provides logical volume information in a configurable form, displaying one line per logical volume.
lvdisplay(8) — Linux manual page
In LVGL, an lv_display_t (not to be confused with a Screen) is a data type that represents a single display panel — the hardware that displays LVGL-rendered pixels on your device. During system initialization, you must do the following for each display panel you want LVGL to use: create an lv_display_t object for it, assign a Flush Callback . lvdisplay [1] allows to Display information about a logical volume (LV) and it is part of Linux LVM implementation. # lvdisplay With no arguments will display all your LVs. # lvdisplay /dev/vg0/lv-0. --- Logical volume --- LV Path /dev/vg0/lv-0. LV Name lv-0. VG Name vg0. This command is used to display information about Logical Volume Manager (LVM) logical volumes. It is a useful tool for managing storage systems and analyzing the configuration of logical volumes. The lvdisplay command provides details such as the logical volume name, volume group, size, allocation type, and more. Command: lvdisplay. We have seen above how to create LV, now we will see how to view details of it. This command is the same as pvdisplay for PV and vgdisplay for VG. It shows you details like name, volume group it belongs to, size, permission, status, allocation policy, etc. # lvdisplay /dev/vg01/lvol1. --- Logical volumes ---
nike anzug damen grau
If you want to see the details of the volume in a Volume Group, you can use the lvdisplay command. Below is an example of lvdisplay command. Here, Vol1 is the Volume Group name. $ sudo lvdisplay Vol1. --- Logical volume --- LV Path /dev/Vol1/lvtest. LV .lvdisplay shows the attributes of LVs, like size, read/write status, snapshot information, etc. lvs (8) is a preferred alternative that shows the same information and more, using a more compact and configurable output format.
golfschuhe nike damen
Display (lv

5.4.13. Displaying Logical Volumes
CREED Aventus. (475) $265.00 - $1,260.00. Best Seller. GIFT WITH PURCHASE. more like this. CREED Aventus 3.3 oz. (473) $495.00. Best Seller. GIFT WITH PURCHASE. .
lv display|Display (lv