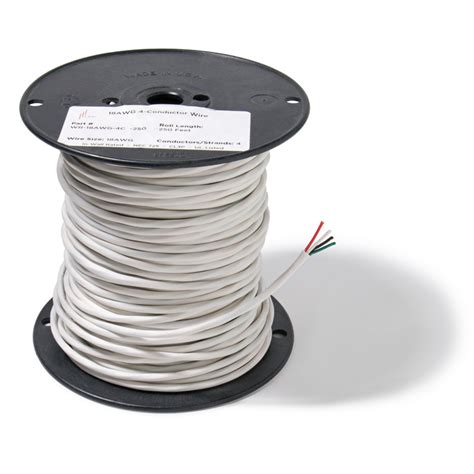
lv wires | immersive engineering wiring guide lv wires Low voltage wiring and cabling transmit data and electrical signals at lower voltages than standard electrical wiring. The cable type is . See more $9.99
0 · low voltage wiring in house
1 · low voltage wiring home depot
2 · low voltage residential house wiring
3 · immersive engineering wiring guide
4 · immersive engineering wire
5 · difference between Lv and hv
6 · Lv wire connector
7 · Lv wire coil
The series of 45 photographs captures the private rooms of Mademoiselle Chanel at 31 rue Cambon in Paris, giving visitors a glimpse at Coco’s fascinating life. “Shooting at Coco Chanel’s apartment was .
Low voltage cable(also called structured cabling or network wiring) is a setup of cables and wiring designed to transmit electrical signals at levels typically below 50 volts. Low voltage wiring consists of twisted pair cables that carry data signals. These low-voltage wires are enclosed in a cable covering to protect . See moreLow voltage wiring and cabling transmit data and electrical signals at lower voltages than standard electrical wiring. The cable type is . See more
Cable is the medium through which information and data move from a separate network device to another. More than a few types of . See more

Businesses that need fast communication between devices can benefit from low-voltage wiring. By facilitating the power transmission of electrical signals below 50 volts, low voltage cable enables the seamless operation of various devices and systems, ranging . See more What Is Low Voltage Wiring? Low-voltage wiring refers to insulated wire with non-metallic sheathing that transmits 50 volts or less of electricity. Standard power outlets in the United States and Canada carry 120V, and .
Low voltage cable (also called structured cabling or network wiring) is a setup of cables and wiring designed to transmit electrical signals at levels typically below 50 volts. Low voltage wiring consists of twisted pair cables that carry data signals. What Is Low Voltage Wiring? Low-voltage wiring refers to insulated wire with non-metallic sheathing that transmits 50 volts or less of electricity. Standard power outlets in the United States and Canada carry 120V, and most lighting fixtures, electronics, and appliances draw up to 120V.
low voltage wiring in house
Usually, LV cables are made up of four components: conductor, insulation, protective sheath, and armor. Next, we understand the important role of each part in detail.

PVC, XLPE, rubber, and control cables are commonly used for LV applications, while XLPE, oil-filled, and gas-insulated cables are used for HV applications. Understanding the different types of LV and HV cables is critical in selecting the right cable for a specific application.LV cables manufactured for excellence. When purchasing low-voltage cables, you want reliability and peak performance built-in. Prysmian Group offers an unrivalled portfolio of low-voltage cables that are manufactured to the highest standards of quality.
What Is Low-Voltage Cable? A low-voltage wire is an electrical cable capable of transmitting 50V of electricity or less. This makes these cables fundamentally different from regular-voltage power cables that transmit 120V/240V AC in the United States and North America and 230V in Europe.
Low voltage cabling refers to the installation of cables and wiring that carry low voltage electrical signals, usually below 50 volts. It is used for a variety of applications including data communication, audio/visual systems, security systems, and lighting control systems.
low voltage wiring home depot
In a low-voltage (LV) plastic-sheathed cable with conductor cross-sections of up to 10 mm2 per conductor or in high-voltage (HV) cables (Figure 2), the lion’s share of the cross-sectional area is occupied by the insulating material.
High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above. As a general rule, LV cables might be used in applications like fixed wiring; MV cables are critical power distribution (both for local grid power and for heavy-duty equipment); HV cables are aerial cables - overhead line for widescale power .We offer an extensive range of 0.6/1.0kV single-core and multi-core power and control low voltage cables. These cables have indoor and outdoor applications in power and petrochemical plants, utility buildings, electrical equipment, and more.
Low voltage cable (also called structured cabling or network wiring) is a setup of cables and wiring designed to transmit electrical signals at levels typically below 50 volts. Low voltage wiring consists of twisted pair cables that carry data signals. What Is Low Voltage Wiring? Low-voltage wiring refers to insulated wire with non-metallic sheathing that transmits 50 volts or less of electricity. Standard power outlets in the United States and Canada carry 120V, and most lighting fixtures, electronics, and appliances draw up to 120V.
Usually, LV cables are made up of four components: conductor, insulation, protective sheath, and armor. Next, we understand the important role of each part in detail.PVC, XLPE, rubber, and control cables are commonly used for LV applications, while XLPE, oil-filled, and gas-insulated cables are used for HV applications. Understanding the different types of LV and HV cables is critical in selecting the right cable for a specific application.
LV cables manufactured for excellence. When purchasing low-voltage cables, you want reliability and peak performance built-in. Prysmian Group offers an unrivalled portfolio of low-voltage cables that are manufactured to the highest standards of quality. What Is Low-Voltage Cable? A low-voltage wire is an electrical cable capable of transmitting 50V of electricity or less. This makes these cables fundamentally different from regular-voltage power cables that transmit 120V/240V AC in the United States and North America and 230V in Europe. Low voltage cabling refers to the installation of cables and wiring that carry low voltage electrical signals, usually below 50 volts. It is used for a variety of applications including data communication, audio/visual systems, security systems, and lighting control systems. In a low-voltage (LV) plastic-sheathed cable with conductor cross-sections of up to 10 mm2 per conductor or in high-voltage (HV) cables (Figure 2), the lion’s share of the cross-sectional area is occupied by the insulating material.
low voltage residential house wiring
High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above. As a general rule, LV cables might be used in applications like fixed wiring; MV cables are critical power distribution (both for local grid power and for heavy-duty equipment); HV cables are aerial cables - overhead line for widescale power .

louis vuitton crossbody fake vs real
louis vuitton belt womens fake
$7,492.00
lv wires|immersive engineering wiring guide